Matlab¶
Dependencies¶
The PaPI-matlab interface needs the following libraries:
| Library | Description |
|---|---|
| libjson | Better handling of json in cpp |
| libboost | Basic boost library |
| libboost-thread | Boost thread support |
| libboost-signals | Boost signal support |
The depencies can be easily fulfilled by installing the following packages:
sudo apt-get install libjsoncpp-dev libboost1.55-dev
sudo apt-get install libboost-thread1.55-dev libboost-signals1.55-dev
Library¶
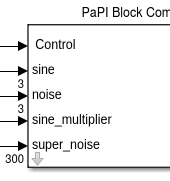
The library is made out of one block:
 |
| The PaPI Block is made of sub system which contains the PaPI Core Block. This blocks provides an easy configurable interface to the core block. |
Input Signals¶
The control input signal is used to control the internal behaviour of the block
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Starts the internal UDPHandle and resets the output signals. |
| 2 | Stops the internal UDPHandle. |
| else | Doesn’t affect the internal behaviour. |
Build¶
All needed functions are compiled and added to the Matlab search path when the build was executed. The build script can be found in </path/to/papi>/PaPI/matlab/ A template template.slx can also be found in the same directory it contains already all necessary changes described in the next section.
After execution the new library PaPI will appear in the simulink library.
Code generation¶
By using the ert_linux it is also possible to build (code generation) a simulink model but it is needed to modify some model settings.
The settings for Code Generation must be edited as following:
Make command:
make_rtw OPTS="-DWITH_HW"
Due to a new version of ert_linux, it is needed to use C89/C90 (ANSI) as default math library. This option can be found in Code Generation/Interface. It is also needed to enable the external mode, can also be found in Code Generation/Interface.
Block Configuration¶
Tab 1¶
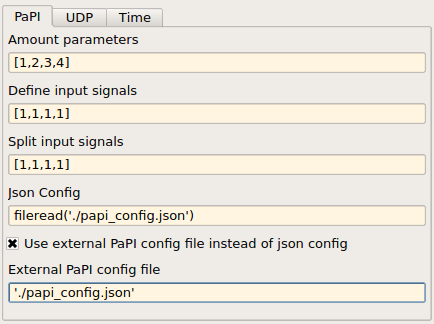
This tab is used to describe the signals and parameters as they appear in PaPI.
The array [1,2,3,4] given in ‘Amount parameters’ leads to 4 different parameters, the parameter dimension is defined by the corresponding array index. Therefore, the first parameter has a size of 1, the second a size of 2, the third a size of 3 and the fourth a size of 4. Is is also possible to name the parameters by setting a signal name in simulink.
The array [1,1,1,1] given in ‘Define input signals’ leads to 4 different signals, the signal dimension is defined by the corresponding array index. Therefore, all signals have a size of one. It is also possible to describe if the signal should be splitted, which is the default case. Having a signal of dimension 4 which should be splitted leads to four different signals in PaPI, if not only one signal with the size four appears in PaPI.
The field ‘Json config’ can be used to provide a configuration which is built in the binary and sent to PaPI when requested. This configuration can be used to control nearly everything in PaPI (create plugins and subscriptions).
Additionally it is possible to set an external configuration file by using ‘External PaPI config file’ and provides the ability to change the configuration during runtime. When an PaPI requests the current configuration this file be read as a source for a json configuration. If it is not possible to parse a json configuration from this file the built-in json configuration will be used.
Parameters¶
|
Signals of the parameters were named in simulink. |
As the parameters will appear in PaPI. |
Naming¶
Tab 2¶

This tab is used set the needed information for the udp communication.
Tab 3¶
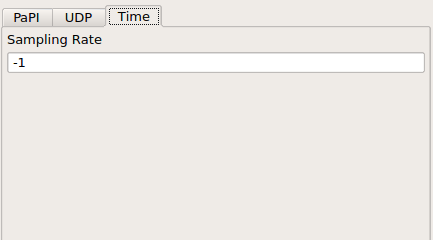
This tab provides the ability to set a sampling rate for the underlying blocks.
Example: Stateflow¶
For stateflow it is necessary to create a simulink function which contains the simulink blocks.
The following picture was taken from the example simulink_example_stateflow which can be found in data_sources/Simulink.
The second input was mapped to the input control of the underlying PaPI Block. At entry the control input is set to one for starting the internal UDPServer of the current PaPI Block. The UDPServer is stopped by setting the control input to two. This must be done when different PaPI Blocks were used because this prevent a single block to occupy the used udp ports forever .
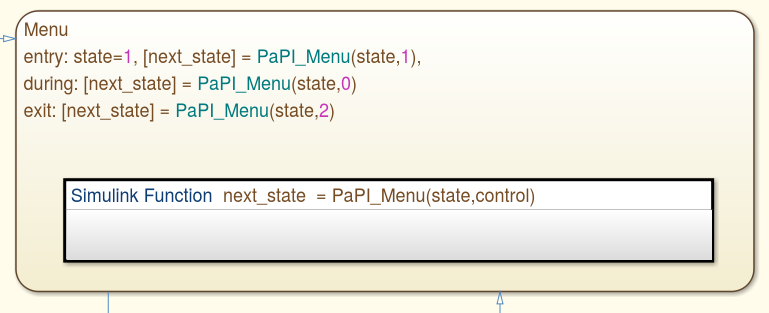
Exemplary use in a state.